The absolute value or modulus of a number x, denoted |x|, is the non-negative value of x without regard to its sign OR it is the distance between this number and the origin of number line.
To understand this definition, substitute any number, such as -3, for the variable a, and read it again:
The modulus of number 3 is the distance from the origin to the point A(3).
That is, the absolute value or modulus is nothing more than a regular distance. Let's try to see the distance from the origin to point A(3)
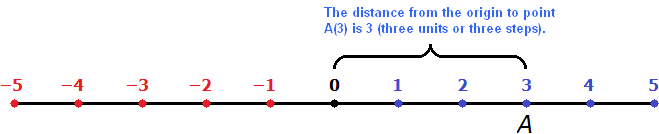
The distance from the origin to point A(3) is 3 (three units or three steps).
The modulus of a number is indicated by two vertical lines, for example:
The modulus of the number 3 is denoted as follows: |3|
The modulus of the number 4 is denoted as follows: |4|
The modulus of the number 5 is denoted as follows: |5|
We searched for the modulus of the number 3 and found out that it is equal to 3. So we write it down:
|3| = 3
Reads as "The modulus of the number three is three".
Now let's try to find the modulus of -3. Again we go back to the definition and substitute the number -3. Only instead of point A we use a new point B. We already used point A in the first example.
The modulus of -3 is the distance from the origin to the point B(-3).
The distance from one point to another cannot be negative. Modulus is also a distance, so it cannot be negative either.
The modulus of -3 is 3. The distance from the origin to point B(-3) is three units:
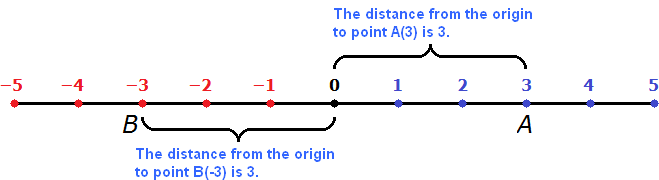
|−3| = 3
It reads "The modulus of the number minus three is three".
The modulus of number 0 is 0, since the point with coordinate 0 coincides with the origin of number line. That is, the distance from the origin to the point O(0) is zero:

|0| = 0
"The modulus of zero is zero"
Let's draw conclusions:
- The modulus of a number cannot be negative;
- For a positive number and zero, the modulus is equal to the number itself, and for a negative number it is equal to the opposite number;
- Opposite numbers have equal modules.
Additive inverse of a number (opposite number)
Numbers that differ only by signs are called opposite
For example, the numbers -2 and 2 are opposite. They differ only in signs. The number -2 has a minus sign, and the number 2 has a plus sign, but we do not see it, because plus, as stated earlier, is not written down.
More examples of opposite numbers:
−1 and 1
−3 and 3
−5 and 5
−9 and 9
Opposite numbers have equal modules.
For example, find the absolute values of the numbers -3 and 3
|−3| and |3|
3 = 3
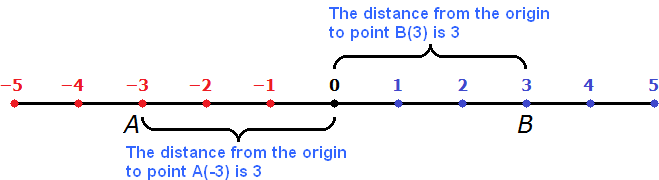
In the figure you can see that the distance from the origin to points A(-3) and B(3) is equal to three steps.
2. If you find an error or inaccuracy, please describe it.
3. Positive feedback is welcome.